PROJECT DESCRIPTION
In this project, a set of experiments was carried out to investigate internal fabrics of granite intrusions with respect to mechanisms of their emplacement and growth. We used a liquid plaster medium as analog material for the magma and dry sand as host rock material. The experiments simulated intrusion emplacement either in static conditions (i.e. without lateral shortening or extension) (Kratinová et al. 2006, 2010) or in an extensional tectonic framework (Mirzaei et al., 2016). The finite internal strain patterns were determined by means of anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility generated by admixed magnetite particles that become aligned in the liquid plaster medium. In the first set of experiments, we employed a simple manual squeezer, where growth of the plutonic body resembled the process of downbuilding of a salt diapir. The solidified bodies of plaster were cut and drilled in a regular grid. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility of the drillcores was finally measured and visualized as maps of internal magnetic fabrics and contour diagrams of the shape (T) and fabric intensity (P) parameters. An animation illustrating the experiment can be viewed here.
For the next series of experiments, we constructed a large sandbox, where the injection of analog magma was driven by a step motor driven piston. The sandbox consisted of two containers connected with a flexible rubber band with small aperture in the center, where the analog magma was injected through a 2.5 cm wide tube. During the experiment, the magma was injected during extension of the central rubber band as the two parts of the sandbox were moved apart by steel ropes attached to a single step motor with a gearbox. Normal or oblique 20% extension experiments resulted in elongated oblate ellipsoidal plutons with rift parallel ridges.
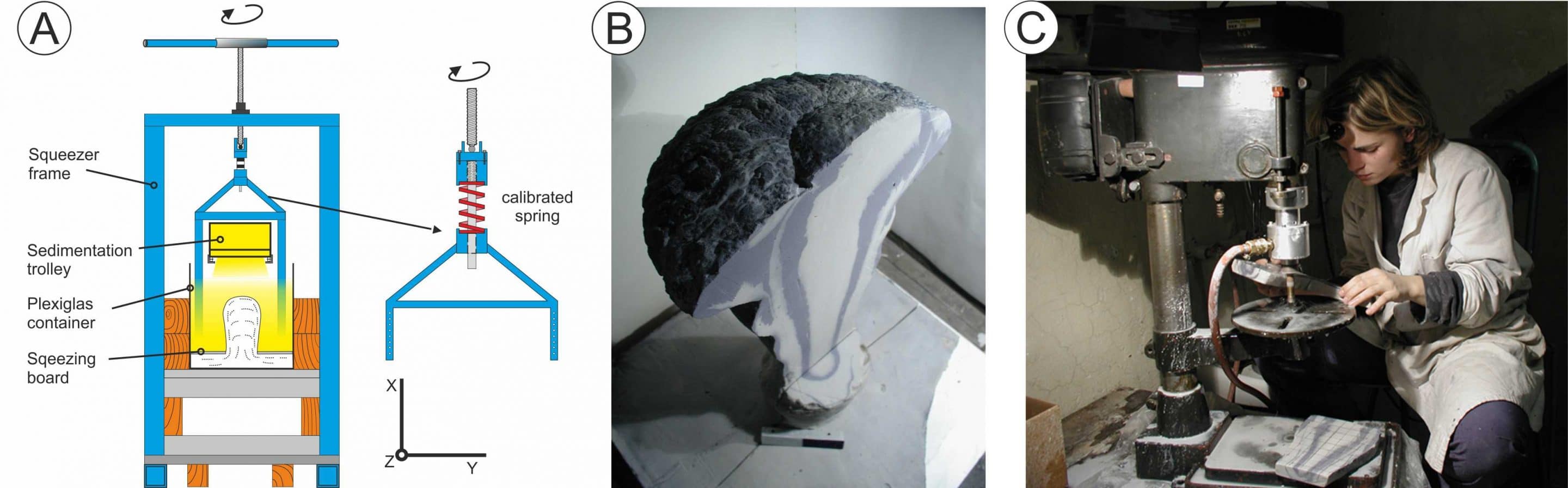
(A) Schematic sketch of the apparatus used for modelling of static intrusions (modified from Kratinova et al., 2006) and (B) the resulting experimental body (scalebar is 10 cm). The apparatus consists of a manual squeezer that loads a board with a circular aperture in the middle. Liquid plaster was evacuated from the bottom part of the container through the board aperture into sand that was continuously sedimented during rise of a columnar body. (C) Drilling of the experimental bodies for the AMS fabric measurements.
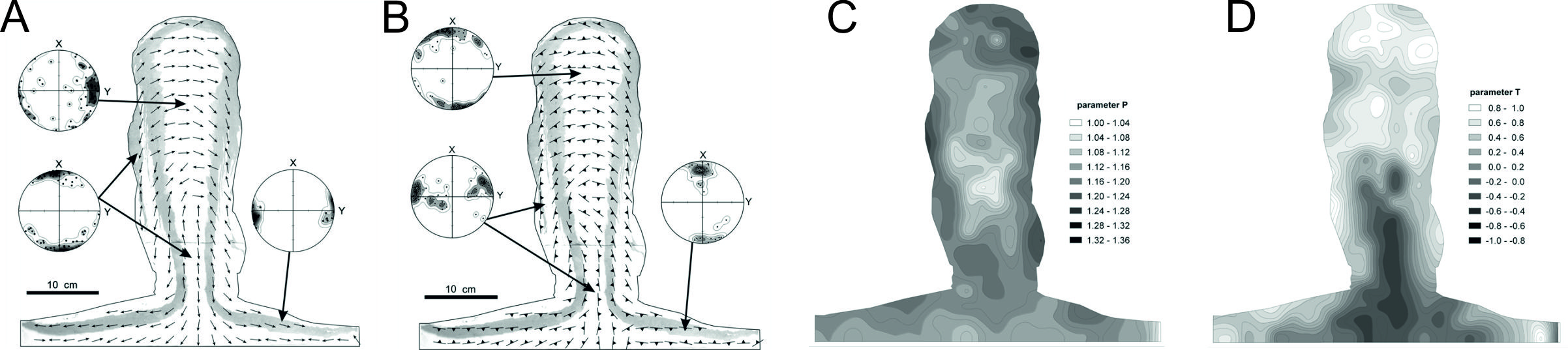
Magnetic fabric in a columnar diapiric body produced in the simple manual squeezer. The first row represents magnetic foliations and lineations and contour diagrams of the shape (T) and anisotropy (P) parameters. Foliations and lineations are also presented in lower hemisphere equal-area projections for selected characteristic domains (modified from Kratinova et al., 2006).
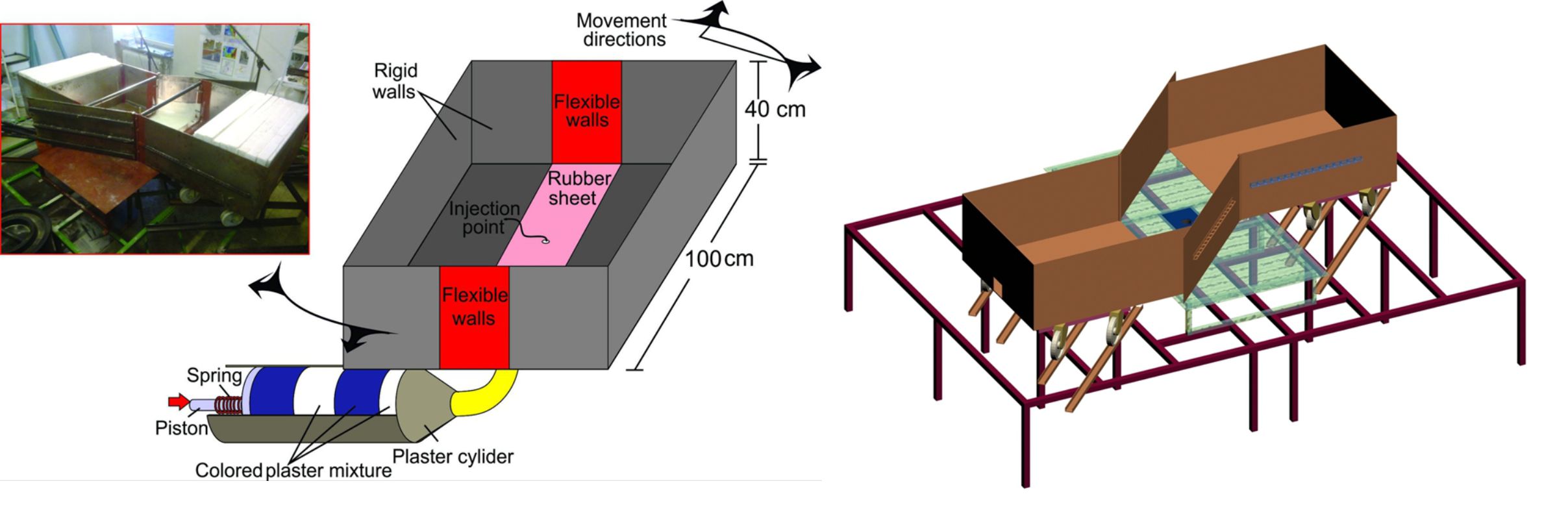
Schematic visualizations of the apparatus used for simulation of simultaneous tectonic deformation and injection of magma.
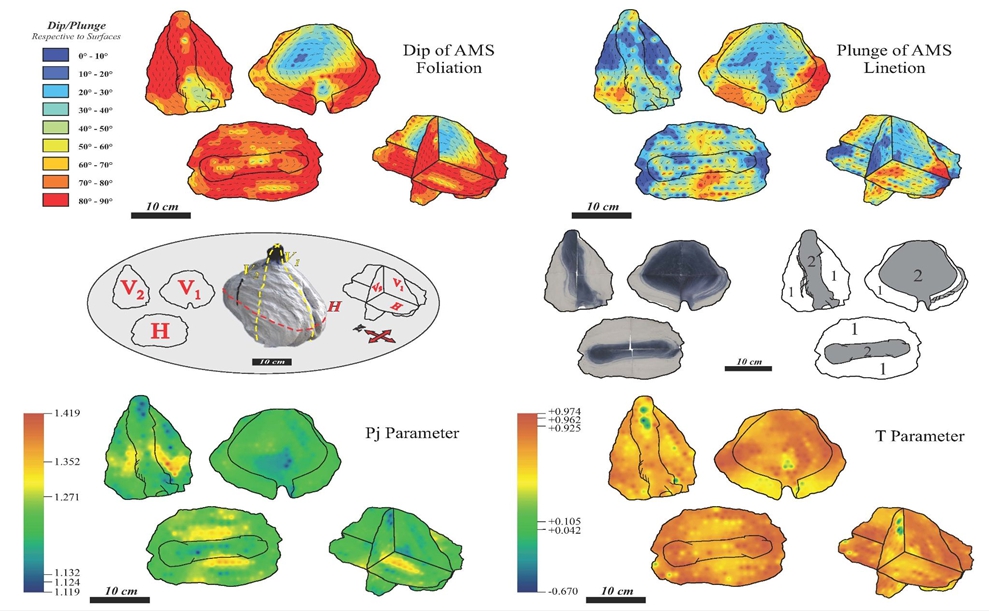
Diagrams illustrating the internal structure of a single experimental magmatic pluton emplaced into sand during oblique extension. The contour diagrams indicate the plunge and dip angles of magnetic lineations and foliations of the investigated sections, as well as P and T parameters (Mirzaei et al., 2016).
Publications
- Kratinova, Z., Machek, M., & Kusbach, V., 2010a. Fabric transpositions in granite plutons—An insight from non-scaled analogue modelling. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 75(1), 267-277, doi: 10.1007/s12594-010-0014-z
- Kratinová, Z., Závada, P., Hrouda, F., & Schulmann, K., 2006. Non-scaled analogue modelling of AMS development during viscous flow: a simulation on diapir-like structures. Tectonophysics, 418(1-2), 51-61, doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2005.12.013
- Mirzaei, M., Závada, P., Kratinová, Z., & Machek, M., 2016. Internal fabrics in magmatic plutons emplaced in extended brittle crust – insight from analogue models with AMS (Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility), In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, EGU2016-17559-1, doi: 10.13140/RG.2.1.4398.6322
Period
2007-2009
Researcher
Zuzana Roxerová
Prokop Závada
Vladimír Kusbach
Matěj Machek
Visitor
- Masoud Mirzaei
Funding
- Grant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (GAAV No. KJB300120702; ‘Fabric transpositions in granite plutons – an insight from non-scaled analogue modelling’)
- FCT project (AMS progress, PTDC/CTE‐GIX/098696/2008)
- Institute of Geophysics of the CAS v.v.i. (No.: AV0Z30120515)


